Atmospheric CO2
only zero carbon only zero carbon only zero carbon only zero carbon only zero carbon only zero carbon only zero only zero
For about 10 000 years before the industrial revolution, the atmospheric abundance of CO2 was nearly constant at ~ 280 ppm (ppm = number of molecules of the gas per million molecules of dry air). This level represented a balance among the atmosphere, the oceans and the biosphere.
The atmospheric CO2 concentration has increased over 50% since industrialization.
As a greenhouse gas CO2 in the atmosphere absorbs and (re-)radiates infra red heat in the lower atmosphere warming the surface of the planet and upper ocean waters.
Today's CO2 from CO2. Earth
The World Meteorological Organizations publishes an annual Greenhouse Gas Bulletin: The State of Greenhouse Gases in the Atmosphere
Atmospheric CO2 is over 422 ppm, (50% increase), the highest in 14 million years
Atmospheric CO2 has been increasing at an accelerating rate throughout its Mauna Loa monitoring record from 1958, and it is presently increasing faster than ever (NOAA link 422 ppm)
Climate science uses two types of CO2 concentrations-
CO2 ppm just CO2 and CO2 equivalent (CO2e or CO2eq).
CO2 equivalent adds in the other main GHGs.
CO2 equivalent (CO2 eq. or CO2 e.) adds in the other GHGs,
most importantly methane and nitrous oxide, as well as
surface ozone and halo-carbons.
2014 IEA Energy Stats 1971-2012
Global Carbon Project Interactive Carbon Atlas
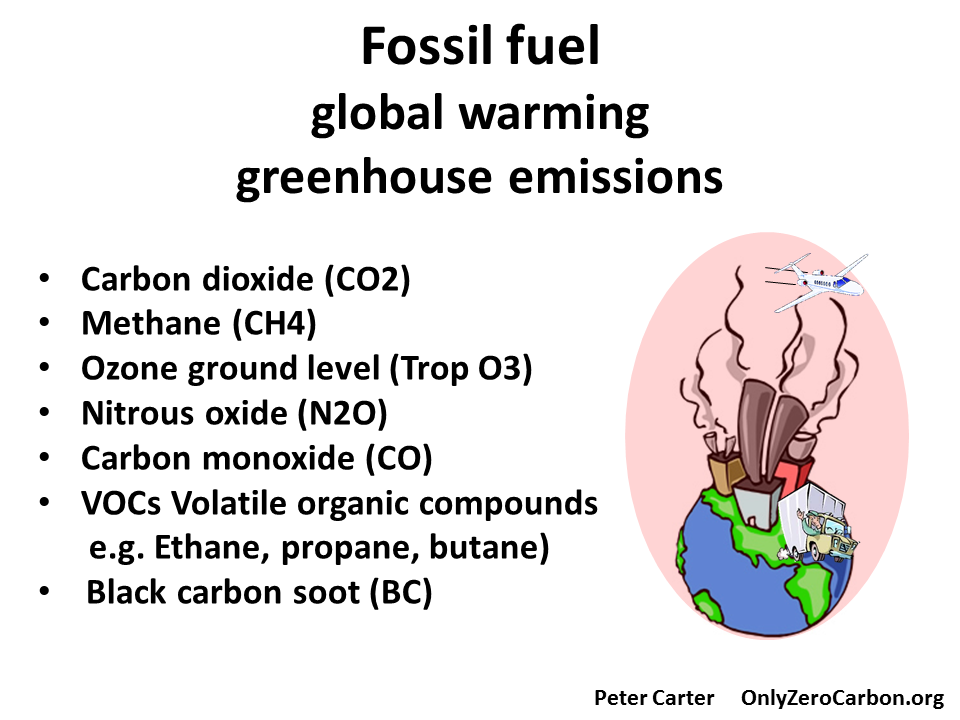
Fossil fuel combustion is by far the top source of CO2 emissions, and is also a source of other global warming GHG emissions; methane (by natural gas), some nitrous oxide, and surface ozone (indirectly).
Atmospheric CO2 has been increasing at an accelerating rate since first monitored in 1958.
It is over 422 ppm (seasonally adjusted means) and is still accelerating today.
Over just 2000 years the abrupt huge atmospheric CO2 increase with industrialization is clear.
Over the past 800,000 years CO2 has never been above 300 ppm. and now it is 422 ppm.
We now know CO2 is the highest in 14 million years
This NOAA site provides monthly concentrations of atmospheric CO2, also methane and nitrous oxide
Scripps Oceanographic Institute monitors atmospheric CO2 at its Moan Loa site, providing daily CO2
Atmospheric CO2 is the main contributor to global heating, 64% of global warming but 80% since 1990 (WMO)
It is the sole cause of ocean acidification
It increases in direct proportion to CO2 emissions, at an accelerating rate- right up to present