ONLY ZERO CARBON ONLY ZERO CARBON ONLY ZERO CARBON ONLY ZERO CARBON ONLY ZERO CARBON ONLY ZERO CARBON
The climate change science of zero carbon is definite, because of the definite basic science of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide lasts in the atmosphere after it has been emitted for an extremely long time.
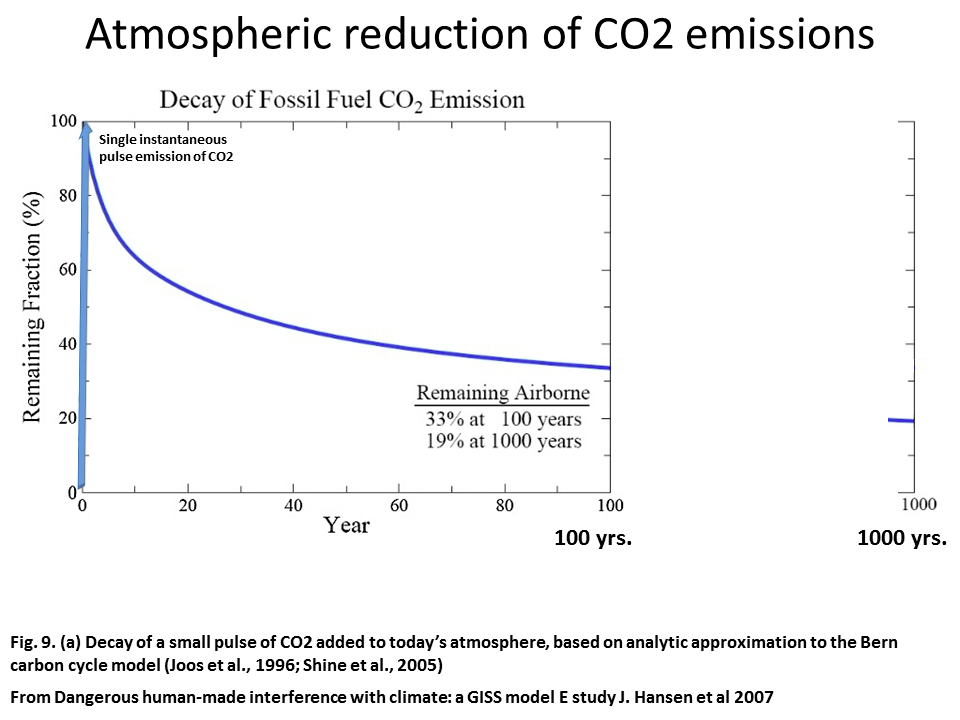
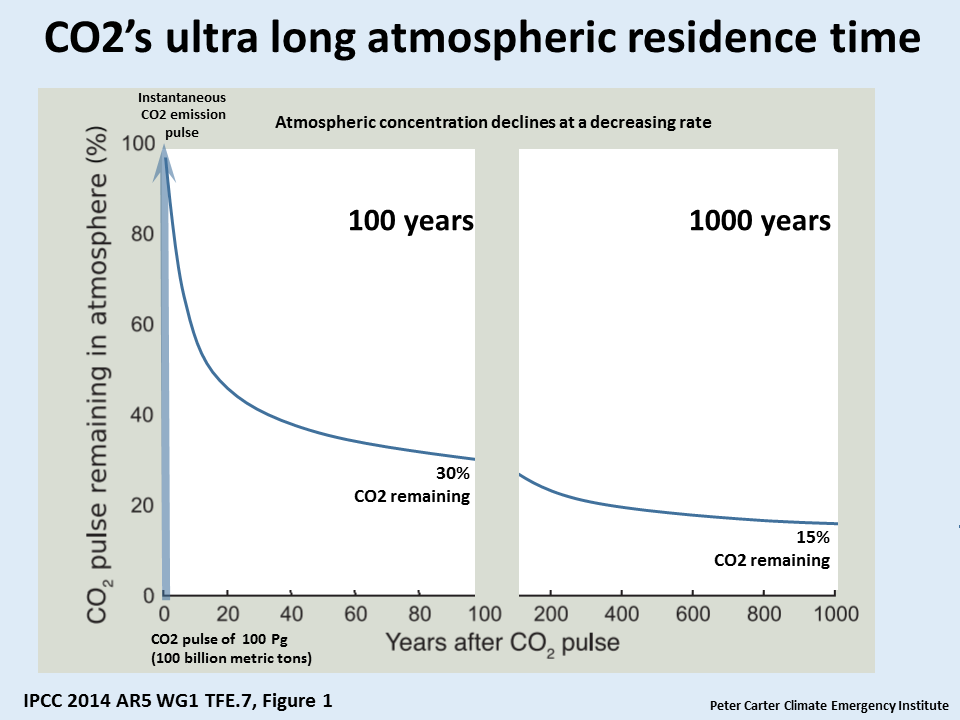
The mean atmospheric life time of CO2 is 200 years, but 33% lasts 100 years and the IPCC says 20% lasts 1000 years. This makes CO2 emissions extremely persistent and so cumulative in the atmosphere.
The science was established many years ago by the the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) that an elevated level of atmospheric carbon dioxide would not drop unless carbon dioxide emissions dropped to zero.
We can understand zero carbon science from what we know above
but over the years some big problems have found their way into climate science.
The result is that net-zero has become a vague formula not based on certain climate and ocean stabilization, and the immediate decline of emissions is not being recommended at all.
The science of CO2 atmospheric persistence means there is always more warming in the pipe to come even near stabilization. Today while global warming is at 1.45°C atmospheric CO2 is highest in 14 million years, the consensus of science is that the 1.5°C limit is still doable. This
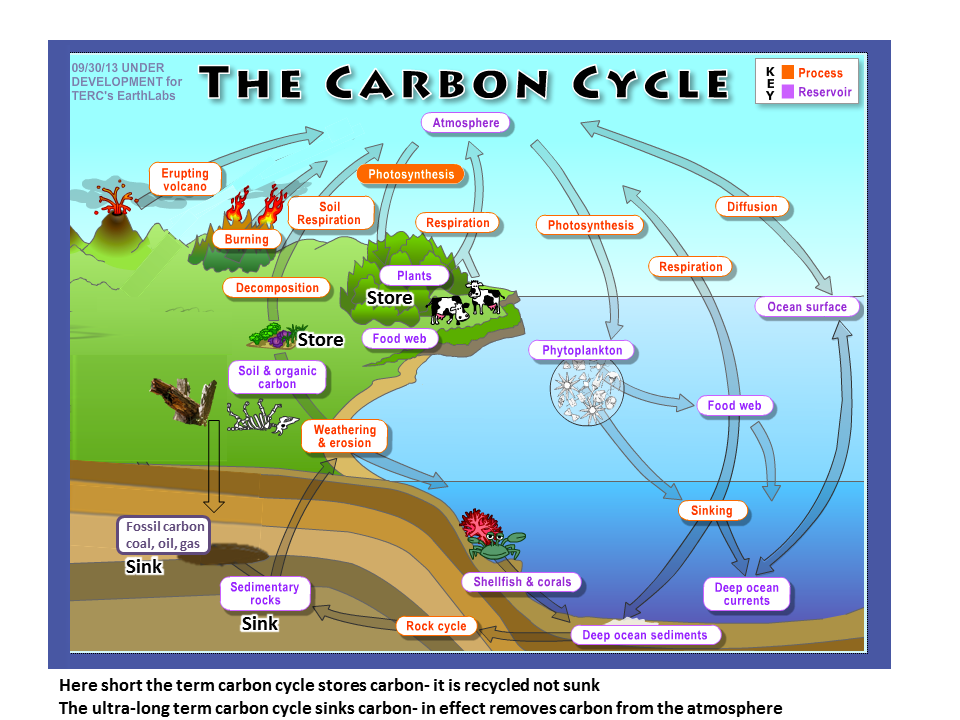
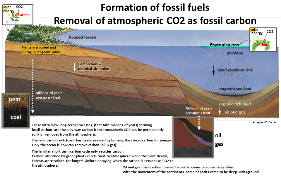
There is much we know. We know the formation of coal oil and gas takes millions of years, which means permanent removal of CO2 from the atmosphere takes million of years by the geologic formation of fossil carbon- fossil fuels (long carbon cycle).
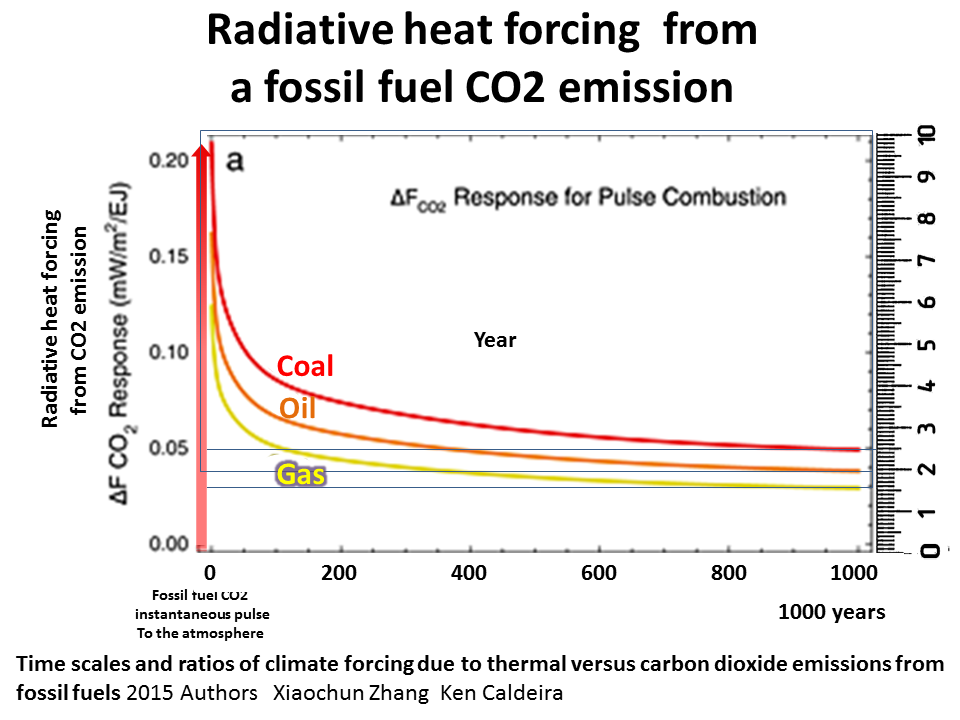
Research shows there is little difference between coal, oil or natural gas in this respect.
Understanding global warming and climate change means understanding that it is a fact that global warming and ocean acidification cannot stabilize, unless our carbon dioxide emissions are dropped to near zero (IPCC 2014).
That is definite due to the very long life-time of CO2 in the atmosphere
So far we have looked at observations determined by climate scientists, and what can be derived by directly applying laws of science.
Carbon feedback
The greatest of all impacts that involves the effect of warming on the planet is not included in projections (still)
That is the large planetary sources of carbon feedbacks, certain at some degree of warming and increasing over time. Warming releases more carbon (CO2 or methane CH4) from soils, vegetation, wetlands, forests (heaat drought stress) forest fires and permafrost.
Risk
Climate change science should be based on risk assessment, but it is not. The risk formula is the product of likelihood and magnitude. Climate science is based on likelihood (model statistical probabilities) but not magnitude. In fact the largest magnitude impacts are not included in the projections. These are the large planetary sources of amplifying feedbacks that includes tipping points.This includes permafrost thaw (methane and CO2) and Amazon forest die-back md increasingly large forest fires. We found years back that rhw model projections were not reliable on timing. Impacts are occuring many years to decades ahead of model projections.
2100 projections
The projections only go to 2100, but warming carries on, albeit slower, for many more 100s of years.
Models
The all important mitigation has become increasingly dependent on computer model programs calculated with great complexity by the scientists.
Until recent years, the scientists pointed out that their models did not predict, they could oly make projections and there would be 'surprises', because the models depended on observed data, which is far from 100% complete or reliable in all cases. Furthermore there is a large range of model projections that gets larger over projected time.
The scientists tae the means of all the projections
Carbon budget
Climate mitigation has focused on the so-called allowable carbon budget by model projections, but (for accuracy) it is not supported by the science The budget applies to CO2 not to the other GHGs. It uses one metric which is cumulative carbon. It does not include amplifying feedbacks or carbon sink efficiency decline.
The budget is based on the assumption that the forest and ocean sinks will be sinking a lot of carbon for us, but the sinks are losing efficiency (Global Carbon Project)
In addition the mitigation projections assume a large reliance on carbon capture and storage (CCS) of fossil fuel combustion emissions and of CCS from the air) negative emissions, which is not science and after decades of trying there is no CCS capacity to capture carbon from fossil fuel combustion or atmosphere.
CCS is still unproven and can never get us anywhere near to zero production.
Today's atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration is over 422 ppm and is rising fast.
To avoid long catastrophic impacts, it has to be dropped too 350 ppm.
There are two fundamental facts of the science:
o The very long atmospheric life-time of CO2, 100s of years
o Ocean heat- over 90% of all added GHG heat is ocean heat with huge ocean heat inertia and momentum
The science has been definite for many years the atmospheric carbon dioxide cannot start to drop unless industrial carbon dioxide emissions are stopped- that's net-zero carbon by zero fossil fuels.
Even virtual zero carbon emissions (like 90%) would not quite stabilize global warming, nor ocean acidification long term.
The science of net-zero carbon for stabilizing
global climate and ocean acidification
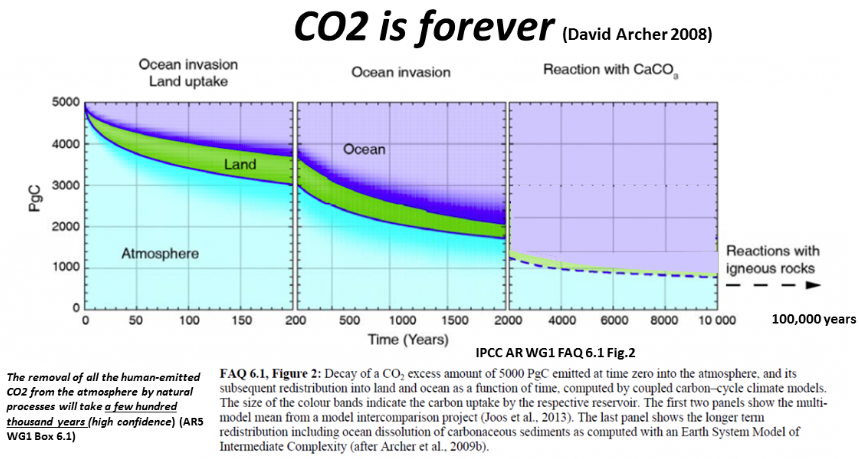
The removal of all human-emitted CO2 from the atmosphere by natural processes will take a few hundred thousand years - (IPCC 2014)
Science
Long atmospheric CO2 life-time - due to ultra-slow removal of CO2
For years it's been reckoned that ater 1000 years 20% of a CO2 emission remains in the atmosphere and in practice it's much longer. Research published back in 2007 Long term fate of anthropogenic carbon, that included some carbon feedback, found about 75% of CO2 emissions have an average perturbation lifetime of 1800 years and 25% have lifetimes much longer than 5000 years and the average perturbation lifetime of atmospheric CO2 is much longer than the 300–400 years proposed by other studies.
Global warming will therefore last over 1000 years
Permanent removal of atmospheric is on a geological time-frame, by the ultra-slow formation of fossil carbon.
There are two scientifically definite imperative objectives for zero or net zero carbon emissions
There is climate stabilization and also oceans stabilization.
While the oceans are being rapidly heated, acidified and de-oxygenated, the state of the oceans is barely considered in climate change mitigation.
The situation today for climate and oceans, as determined by the climate scientists for sure, is stunning
Atmospheric CO2 is at a 14 million year high, having increased 50%.
It is increasing at an unprecedented rate in tens of millions of years
Ocean acidification has increased 25% with industrialization and is the highest in at least 2 million years (EPA)
It is increasing faster than the past 300 million years
For multiple reason the science reinforces the fact, that as the IPCC says, for stabilization to limit global warming to 2°C and 1.5°C global emissions must decline fast starting immediately. The main reason is CO2 emissions last 100s of years in the atmosphere, making CO2 emissions highly persistent and cumulative.
However this is not being recommended, instead the carbon budget is being used based on a cumulative carbon limit, not a time limit. The limit is often expressed as emissions peak.
In fact starting with the IPCC 2007 Assessment climate science to us that global emissions had to be in decline by 2020 - for the 2°C limit. Here is an example from IPCC in 2018 of the 2020 lime limit.
Climate scientists today say that technology can get around the slow natural CO2 removal- CCS
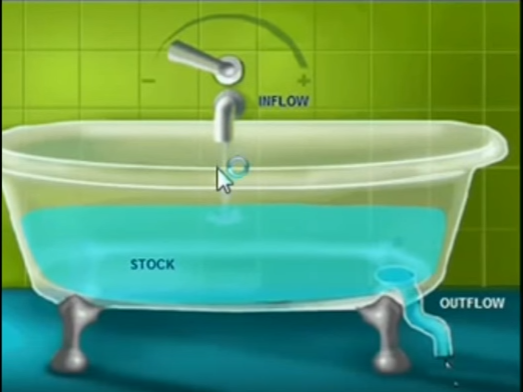
The bathtub analogy to show
stabilization requires no fossil fuel industrial carbon emissions VIDEO